Microfluidic fiber chips can be broadly divided into:
- Bilateral implantation of optical fiber
- Unilateral implantation of optical fiber
Bilateral implantation of optical fiber: it isn’t easy to align two fiber cores precisely and perpendicular to the channel, but it can be tested by simply passing the fluorescent signal transmitted through the fiber through a filter and connecting it to the Photomultiplier tubes.
Unilateral implantation of optical fiber: the fabrication process of unilateral implantation of optical fiber chips is relatively simple, but the detection process is complicated. The chips need to be placed in a dark box close to the photomultiplier tubes or photodiode, which is not easy to operate.
Bilateral implantation of optical fiber
The microfluidic and fiber channels were fabricated on the glass substrate, and then PDMS was poured on the mold. Remove the mold after curing. The microfluidic channel and the fiber channel were fabricated. The treated two fibers were embedded in the fiber channel and glued to another glass piece.
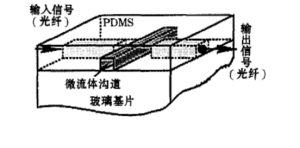
Unilateral implantation of optical fiber
The critical point of fabricating unilateral implantation of optical fiber chips is to embed tiny avalanche photodiode in the PDMS at the bottom of the microfluidic channel to detect fluorescent signals.
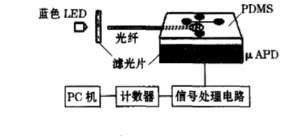
Advantages of unilateral optical fiber: long lifetime, low loss, high-quality signal transmission, and maximum bandwidth distance product. But the optical core is not easy to align because of its small aperture, and the effect of waveguide dispersion in single-mode fiber is very significant.
Advantages of multi-mode optical fiber: through using multi-mode fiber with a larger core radius, optical power can be easily injected into the same fiber and connected.
